Remanufacturing
Remanufacturing plays a vital role in the circular economy by closing product loops while preserving or restoring the original design and functional properties of products—thus enabling their reuse. The process begins with the disassembly of used products (known as cores), followed by cleaning and sorting of individual components. These parts are then remanufactured and reassembled into products that meet "as-new" standards.
Unlike simple repair, remanufacturing is an industrial-scale process that restores products to at least the quality level of new ones, effectively initiating a new product life cycle.
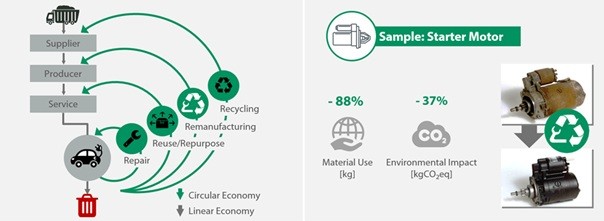
Remanufacturing offers significant environmental, economic, and social benefits. For example, material consumption and environmental impact can be reduced by up to 88% and 37%, respectively, in the case of starter motors. Additionally, remanufactured products are typically priced 40% to 80% lower than their new counterparts, making them a cost-effective alternative.
To successfully implement remanufacturing in industrial practice, it is essential to consider the entire product life cycle. At the Chair Manufacturing and Remanufacturing Technology (LUP), innovative solutions are being researched and developed to support this goal. Scientists at LUP collaborate closely and across disciplines with partners from academia and industry to drive progress in this field.